

All exception and error types are subclasses of the base class of the hierarchy, Throwable. Exception is in charge of one branch. This class is used to represent exceptional conditions that user programs should be aware of. An example of such an exception is NullPointerException. Another branch, Error, is used by the Java run-time system (JVM) to indicate run-time environment errors (JRE).
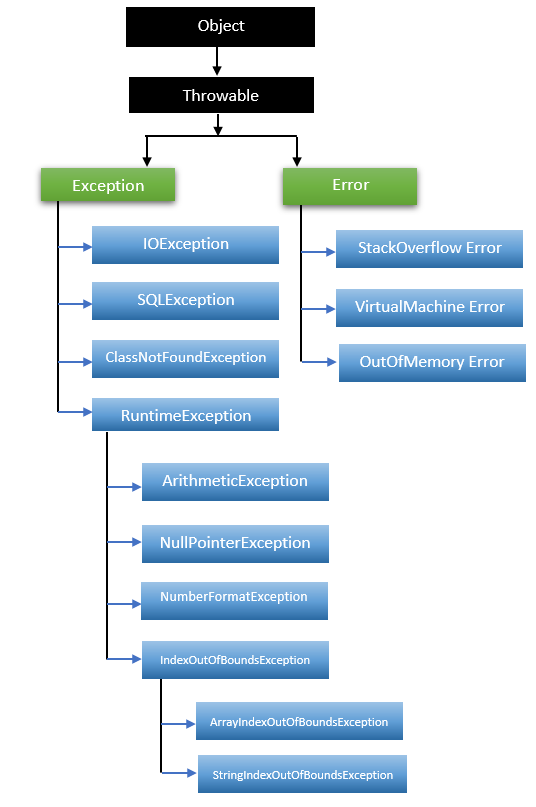
Java defines several exception types that are related to its various class libraries. Users can also define their own exceptions in Java.
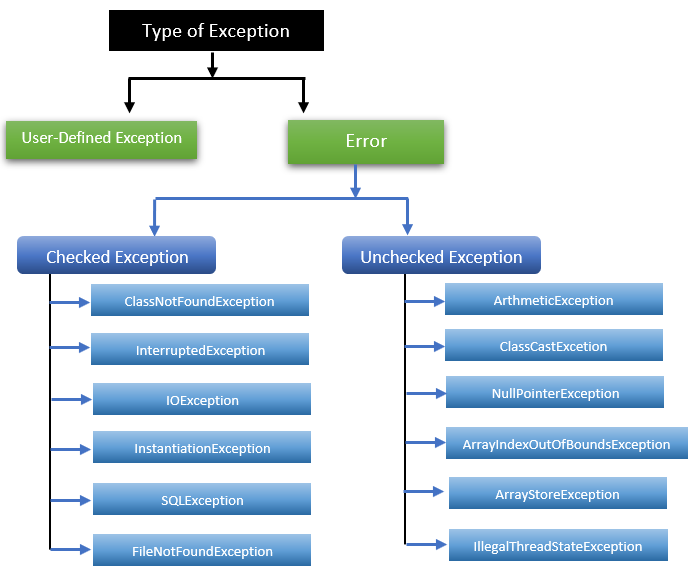
Java provides five keywords for dealing with exceptions are mention below
| Keyword | Description |
|---|---|
| try | The "try" keyword is used to specify a block where an exception code should be placed. That means we can't just use the try block. The try block must be followed by a catch or finally block. |
| catch | The exception is dealt with using the "catch" block. It is essential to include a try block before using a catch block. Additionally, the finally block can be utilized to execute code that should follow the try-catch block |
| throw | To throw an exception, we use the "throw" keyword. |
| throws | To specify exceptions, use the "throws" keyword. It makes clear that the method could encounter an exception. No exception is thrown by it. It is constantly utilized with method signatures. |
| finally | The program's necessary code is executed using the "finally" block. Whether or not an exception is handled, it is still executed. |
public class Main { public static void main(String args[]){ try{ int Num=50/0; //code inside try block may raise exception } catch(ArithmeticException e){ System.out.println(e); } // code below catch block will execute normally System.out.println("This Code is unaffected to exception handling"); } }
A try-catch block is used to handle an ArithmeticException that is raised by 50/0.
Output:
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
This Code is unaffected to exception handling
1. printStackTrace() : The format of the information printed by this method for exceptions is Name of the exception, Description of the exception, and Stack Trace.
package DockerTpoint; public class Main { public static void main(String args[]){ try{ int Num=10/0; //code inside try block may raise exception System.out.println(Num); } catch(ArithmeticException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } // code below catch block will execute normally System.out.println("This Code is unaffected to exception handling"); } }
Output:
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at HELLO/DockerTpoint.Main.main(Main.java:5)
This Code is unaffected to exception handling
2. toString() : The format of the information printed by this method is Name of the exception.
package DockerTpoint; public class Main { public static void main(String args[]){ try{ int Num=10/0; //code inside try block may raise exception System.out.println(Num); } catch(ArithmeticException e){ System.out.println(e.toString()); } // code below catch block will execute normally System.out.println("This Code is unaffected to exception handling"); } }
Output:
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
This Code is unaffected to exception handling
package DockerTpoint; public class Main { public static void main(String args[]){ try{ int Num=10/0; //code inside try block may raise exception System.out.println(Num); } catch(ArithmeticException e){ System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } // code below catch block will execute normally System.out.println("This Code is unaffected to exception handling"); } }
Output:
/ by zero
This Code is unaffected to exception handling
public class Main { public static void main(String args[]){ try{ int Num=50/0; //code inside try block may raise exception } catch(ArithmeticException e){ System.out.println(e); } // code below catch block will execute normally System.out.println("This Code is unaffected to exception handling"); } }
Output:
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
This Code is unaffected to exception handling
public class Main { public static void main(String args[]){ try{ String str=null; //code inside try block may raise exception System.out.println(str.length()); } catch( NullPointerException e){ System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } // code below catch block will execute normally System.out.println("This Code is unaffected to exception handling"); } }
Output:
Cannot invoke "String.length()" because "str" is null
This Code is unaffected to exception handling
public class Main { public static void main(String args[]){ try{ String str=null; //code inside try block may raise exception int i=Integer.parseInt(str); System.out.println(i); } catch( NumberFormatException e){ System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } // code below catch block will execute normally System.out.println("This Code is unaffected to exception handling"); } }
Output:
Cannot parse null string
This Code is unaffected to exception handling
public class Main { public static void main(String args[]){ try{ int a[]=new int[10]; //code inside try block may raise exception a[15]=500; } catch( ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } // code below catch block will execute normally System.out.println("This Code is unaffected to exception handling"); } }
Output:
Index 15 out of bounds for length 10
This Code is unaffected to exception handling
Post your comment